Copper products have been used by man for several centuries. In pre-revolutionary times, the price of this metal was equated to the cost of gold, its production was so expensive. Now copper has become much cheaper, so from it, in addition to jewelry, make dishes, interior accessories and other items.
- What is corrosion of metals and alloys
- Corrosive properties of copper
- Fracture Conditions
- Water effect
- Exposure to Acids and Alkalis
- Corrosion in soil and moist air
- Why do copper products need regular cleaning?
- Effective Copper Cleaning Methods
- Cleaning coins from copper

Corrosion of copper, unlike iron, develops slowly due to its resistance to this phenomenon, and yet sometimes it is necessary to take measures to clean products from ugly deposits.
What is corrosion of metals and alloys
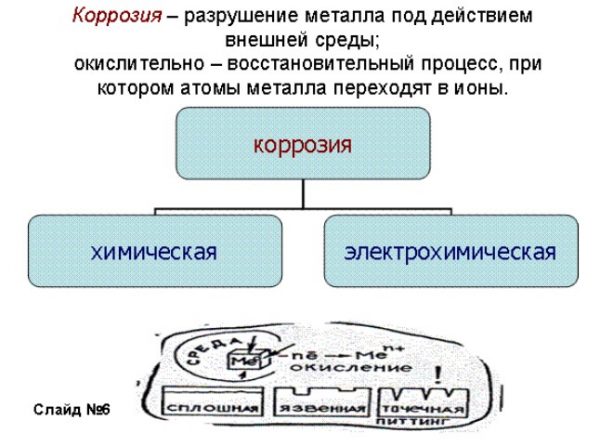
Corrosion is understood as the process of metal destruction under the influence of aggressive environmental factors. To one degree or another, all metals and alloys rust, as a result of which rust and areas of integrity damage (holes) appear on them. Non-metals can also deteriorate over time: aging rubber or plastic from interaction with oxygen, with frequent contact with water, and temperature changes can be an example.
The main cause of corrosion is the thermodynamic instability of the metal to the influence of physical factors or chemicals that are present in the contact medium. Compared with iron, copper is much less oxidized, but with increasing temperature, this process is significantly accelerated. When regularly located in an environment with a temperature above +100 degrees, any metal rusts several times faster.
to contents ↑Corrosive properties of copper
Copper is a metal with high plastic properties, having a red-gold color, and after removing the oxide film - a little pinkish. It is second only to silver in electrical conductivity and is also characterized by high thermal conductivity. Due to its low specific resistance, copper is used in electrical engineering: it is used for the manufacture of copper plates, wire, and motor windings.
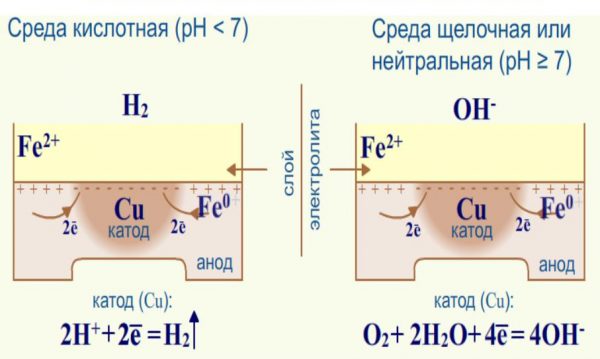
Due to the high anticorrosive qualities, metal is included in alloys to improve their technical characteristics (bronze, brass and others). In a galvanic medium, copper becomes a cathode, enters into electrochemical processes and causes accelerated rusting of other metals.
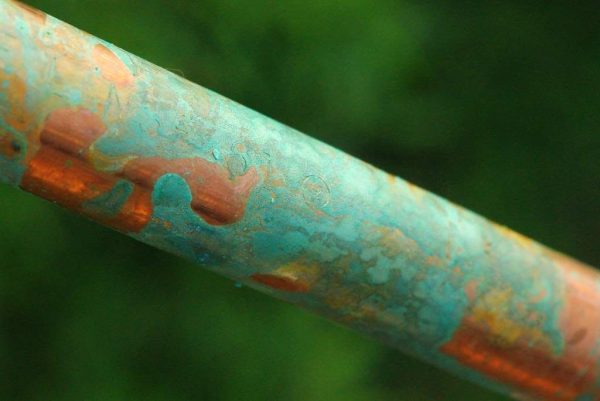
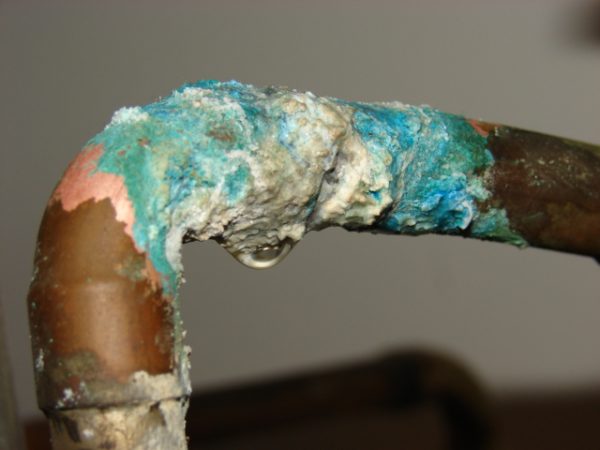
Copper is an inactive chemical element, and therefore practically does not interact with air, water (fresh, marine). If the air is dry, an oxide film up to 50 mn thick is formed on the surface of the material. A copper product darkens, turns brown or greenish, this is called a patina. In some cases, patina is perceived as a decorative coating. The corrosion rate is low when in contact with dilute hydrochloric acid, but when reacted with a number of other acids, with halogens, “aqua regia”, the metal oxidizes to form copper carbonate.
to contents ↑Fracture Conditions
Despite its resistance to spoilage, even copper products can rust under certain conditions. These phenomena are least pronounced in moist air, water, soil, and more in acidic environments.
Corrosion can be seriously reduced by tinning - coating copper with a layer of tin. High-quality tinning provides reliable protection against damage, increases corrosion resistance, makes the material not subject to high temperatures, rain, hail, snow. The service life of tinned products is more than 100 years without loss of original properties.
to contents ↑Water effect
The corrosion rate of copper in water strongly depends on the presence of an oxide film on its surface, as well as on the degree of saturation of water with oxygen. The higher the content of the latter, the more intensive the destruction of the material. In general, copper is considered resistant to the harmful effects of salt and fresh water, and only dissolved chlorine ions, low pH, adversely affect it. Strength, resistance to rust allows the use of material for the manufacture of pipelines.
If a brown or green oxide peel is present on the surface of a copper-coated product, the destructive substances penetrate to a small extent. Typically, an oxide layer is formed after 60 days the metal is in water. Green peel (carbonate) is considered more durable, loose and less strong - black (sulfate).
In sea water, the level of corrosion is almost the same as in fresh water. Only when accelerating the movement of a fluid does corrosion become shock, and therefore more intense. Copper is a material that is not capable of overgrowing marine microorganisms, because its ions are harmful to mollusks and algae. This metal property is used in shipping and fisheries.
to contents ↑Exposure to Acids and Alkalis
In alkalis, copper does not deteriorate, because the material itself is alkaline, but the acids for it are the most harmful in effect. The most significant and rapid corrosion occurs upon contact with sulfur and its acid compounds, and nitric acid completely destroys the structure of the material.
Copper dissolves in concentrated acids, therefore, in the manufacture of equipment for the oil and gas industry requires additional protection. For this purpose, inhibitors - inhibitors of chemical reactions are used:
- Shielding - form a film that prevents acids from reaching the copper surface.
- Oxidizing - turn the top layer into oxide, which will react with acids without harm to the metal itself.
- Cathode - increase the cathode overvoltage, which slows down the reaction.
Corrosion in soil and moist air
There are many microorganisms in the soil that produce hydrogen sulfide, so the environment is acidic, the corrosion rate of copper increases. The more the pH value is deviated towards acidification, the faster the destruction processes occur. If the soil is saturated with oxygen, the metal oxidizes, but less rust. When copper products are in the ground for a long time, they turn green, become loose and can even crumble. A short stay in the soil causes the appearance of patina, from which the subject can be cleaned.
to contents ↑Wet air adversely affects the condition of the material only with prolonged contact, and at first also causes the appearance of a patina (oxide layer). The exception is steam saturated with chlorides, sulfides, carbon dioxide - corrosion develops more rapidly in it.
Why do copper products need regular cleaning?
Copper Turks, ladles, samovars are characterized by high thermal conductivity, so the heating in them proceeds evenly, and the products cook faster. This leads to a high popularity of household products. The need for cleaning copper items is due to the loss of their external attractiveness over time. Especially quickly fade and lose their natural color products that are in the air or often heated.
Oxide film - patina - is popular only where it is necessary to give things a vintage look, antique styling. Otherwise, it spoils the look of dishes, utensils, jewelry and figurines. To eliminate oxide deposits, darkening elements and restore shine, you will have to periodically clean items. Cleansing is also required to prevent the ingestion of harmful compounds that may be present in the black or green layer.
to contents ↑Effective Copper Cleaning Methods
It is not difficult to clean copper objects; expensive means will not be needed for this. Here are the most popular methods used at home:
- Ketchup. Take a little tomato ketchup, grease the product with it, leave for two minutes. After rinse with a stream of water.
- Dishwashing solution. Lather the household sponge with the usual dishwashing liquid, wipe the surface thoroughly, and rinse with water. This method is best for products that have only slightly faded.
- Lemon. Grate the copper surface with a slice of lemon, then go over it with a brush with hard bristles and wash with water.
- Vinegar and flour. Pour a little vinegar into a cup, add flour until a dough of medium density is obtained. Lubricate the copper with dough, leave to dry, then remove the residues, and rub the product with a soft cloth.
- Vinegar and salt. Pour 9% vinegar into a stainless steel pan, add a little salt, let it boil. Turn off the fire, put a copper object in the solution, do not remove it until the liquid cools. This method is suitable for heavily soiled surfaces.
Cleaning coins from copper
Copper coins are antiques, and in our time are not issued. Often they have to be cleaned to return an attractive look. If the coin is in contact with lead, the coating on it may be yellowish. In this case, it is perfectly cleaned with table vinegar (9%). Green plaque is removed with a solution of citric acid (10%) or lemon juice, brown - with ammonia, ammonium carbonate.
It must be remembered that sometimes the patina layer gives the coins a more noble and vintage look, therefore it is not always advisable to remove it. Some, by contrast, try to artificially age money at home. To do this, take a liter of distilled water, 5 g of pharmaceutical potassium permanganate, 50 g of copper sulfate. Heat the solution without boiling, toss coins into it, leave until the desired color is achieved. To fix the effect, treat the dried money with a mixture of benzene and alcohol (1: 1). After the coin will find a beautiful aged appearance and will be able to decorate any collection of antiques.