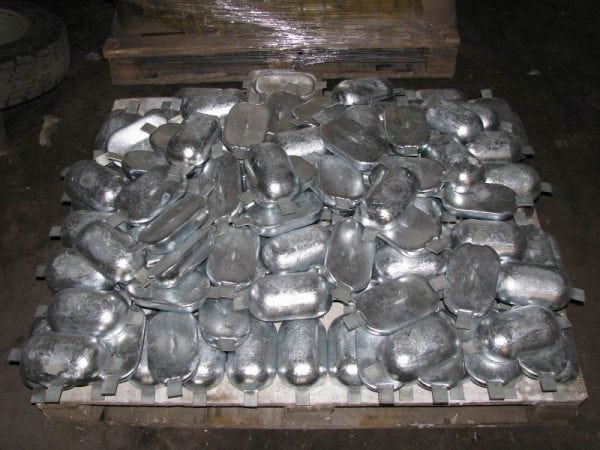
Tread protection is one of the possible options for protecting pipeline structural materials from corrosion. It is used primarily on gas pipelines and other highways.
The essence of tread protection
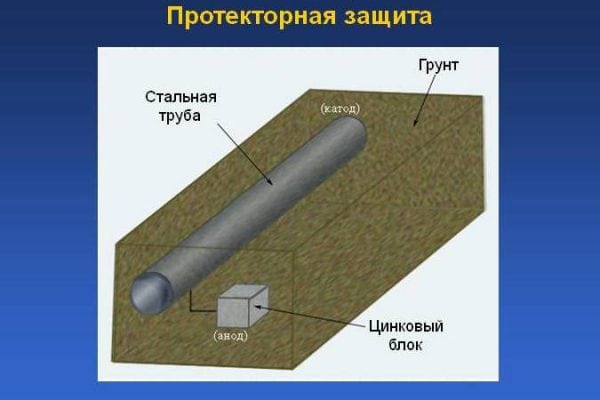
Tread protection is the use of a special substance - an inhibitor, which is a metal with increased electronegative qualities. Under the influence of air, the tread dissolves, as a result of which the base metal is preserved, despite the influence of corrosive factors. Protective protection is one of the varieties of the cathodic electrochemical method.
This version of anti-corrosion coatings is especially often used when an enterprise is constrained in its ability to organize cathodic protection against corrosion processes of an electrochemical nature. For example, if the financial or technological capabilities of the enterprise do not allow the construction of power lines.
A tread inhibitor is effective when the index of transition resistance between the protected object and the environment around it is not significant. High tread performance is possible only at a certain distance. To identify this distance, the definition of the radius of the anticorrosive action of the applied tread is applied. This concept shows the maximum removal of the protective metal from the protected surface.
The essence of corrosion processes is that the least active metal during the interaction period attracts the electrons of the more active metal to its own ions. Thus, at the same time two processes are carried out at once:
- reduction processes in a metal with less activity (in the cathode);
- oxidation processes of the anode metal with minimal activity, due to which the pipeline (or other steel structure) is protected from corrosion.
After some time, the effectiveness of the tread decreases (due to loss of contact with the protected metal or due to dissolution of the protective component). For this reason, there is a need to replace the tread.
to contents ↑Method Features
Protectors for protection against corrosive processes in acidic environments are meaningless. In such media, the dissolution of the tread occurs at a faster pace. The technique is recommended for use only in neutral environments.
In comparison with steel, metals such as chromium, zinc, magnesium, cadmium, as well as some others, are more active. In theory, it is these metals that should be used to protect pipelines and other metal structures. However, there are a number of features, knowing which, you can justify the technological meaninglessness of the use of pure metals as protection.
For example, magnesium is characterized by a high rate of corrosion development, a thick oxide film is rapidly formed on aluminum, and zinc dissolves very unevenly due to its special coarse-grained structure. In order to negate such negative properties of pure metals, alloying elements are added to them. In other words, the protection of gas pipelines and other metal structures is carried out through the use of all kinds of alloys.
Often used magnesium alloys.In addition to the main component - magnesium - they contain aluminum (5-7%) and zinc (2-5%). In addition, small amounts of nickel, copper and lead are added. Magnesium alloys are relevant for corrosion protection in environments where the pH does not exceed 10.5 units (traditional soil, fresh and slightly saline water bodies). This limiting indicator is associated with the fast solubility of magnesium in the first stage and the subsequent appearance of sparingly soluble compounds.
Note! Magnesium alloys often cause cracks in metal products and increase their hydrogen brittleness.
For structures made of metals located in salt water (for example, an underwater pipeline), protectors based on zinc should be used. Such alloys also contain:
- aluminum (up to 0.5%);
- cadmium (up to 0.15%);
- copper and lead (up to a total of 0.005%).
In an aqueous salt environment, the protection of metals from corrosion using zinc-based alloys would be the best option. However, in fresh water bodies and on ordinary soil, such protectors very quickly become overgrown with oxides and hydroxides, as a result of which anti-corrosion measures lose their meaning.
Zinc-based protectors are more often used to protect against corrosion those metal structures where technological conditions require the highest degree of fire safety and explosion safety. An example of the demand for such alloys are gas pipelines and pipelines for transporting flammable liquids.
In addition, zinc compositions, as a result of anodic dissolution, do not form pollutants. Therefore, such alloys are practically uncontested when it is necessary to protect the pipeline for transporting oil or metal in tanker vessels.
In conditions of salt running water on the coastal shelf, aluminum alloys are often used. Such formulations include cadmium, thallium, indium, silicon (up to 0.02% in total), as well as magnesium (up to 5%) and zinc (up to 8%). The tread properties of aluminum compounds are similar to those of magnesium alloys.
to contents ↑Combination of protectors and paints
Often there is a need to protect the gas pipeline from corrosion not only by the tread, but by paint and varnish. Paint is considered a passive method of protection against corrosion processes and is really effective only when combined with the use of a tread.
This combination technique allows you to:
- Reduce the negative impact of potential flaws in the coating of metal structures (peeling, swelling, cracking, swelling and the like). Such flaws exist not only as a result of factory defects, but also due to natural factors.
- Reduce (sometimes by a very significant amount) the consumption of expensive protectors, while increasing their lifespan.
- Make the distribution over the metal of the protective layer more uniform.
It is also worth noting that paints and varnishes are often very difficult to apply to certain surfaces of an already operating gas pipeline, tanker, or some other metal structure. In such cases, you will have to do only with a protective tread.









