The method of steel oxidation is an action aimed at the formation of an oxide film on a metal surface. The task of oxidation is to create coatings that will carry a decorative and protective function. In addition, dielectric coatings are formed on steel structures using oxidation.
- Features of oxidation
- Chemical way
- Anodic oxidation
- Features of plasma and thermal processes
- Self oxidation
- Protection of titanium and its alloys
- Silver surface protection
- Brass surface protection

Features of oxidation
There are several ways to oxidize:
- chemical;
- Plasma
- thermal;
- electrochemical.
Chemical way
Chemical oxidation means surface treatment with special melts, nitrate, chromate solutions, as well as other oxidizing agents. As a result, it is possible to increase the corrosion resistance of the metal. Such events are carried out using acidic or alkaline formulations.
Alkaline oxidation is carried out at temperatures of 30-180 degrees. The main component of the compositions is alkali, and very few oxidants are added. After the procedure, the parts are washed and dried. Sometimes after oxidation, oiling is carried out.
Acid oxidation is carried out using several acids (phosphoric, hydrochloric, nitric) and small amounts of manganese. The temperature regime of the process is 30-100 degrees.
Chemical oxidation of these varieties makes it possible to obtain a film of good quality. Although it should be noted that the electrochemical method allows to obtain products of higher quality.
Cold oxidation (blackening) is also a chemical technique. It is carried out by dipping the part into the solution with further washing, drying and oiling. As a result, a crystalline structure is formed on the surface with the presence of phosphates and ions. A feature of the technology is the relatively low operating temperature (15-25 degrees Celsius).
Advantages of blackening in comparison with hot oxidation:
- details only slightly change their sizes;
- lower energy consumption;
- high level of security;
- no fumes;
- products have a more uniform color;
- the technique allows even cast iron to be oxidized.
Anodic oxidation
Electrochemical oxidation (anode technique) is carried out in a liquid or solid electrolyte medium. This approach allows to obtain films of high strength of the following types:
- coatings with a thin layer (thickness - 0.1-0.4 microns);
- wear insulators resistant to wear (thickness - 2-3 microns);
- protective coatings (thickness 0.3-15 microns);
- special enamel layers (enamel coatings).
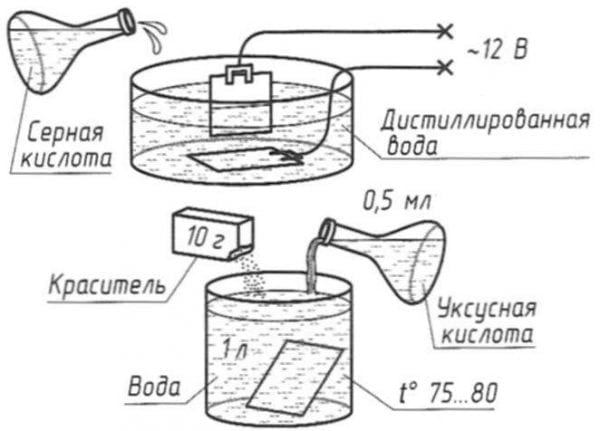
The anodizing of the surface of the oxidized part is carried out against the background of a positive potential. Such processing should be carried out in order to protect parts of microcircuits, as well as to create a dielectric layer on semiconductors, steel, metal alloys.
Note! If necessary, anodizing can be carried out independently, however, it is necessary to strictly adhere to safety regulations, since aggressive elements are used in the work.
A special case of electrochemical oxidation is microarc oxidation.The technique makes it possible to achieve unique decorative properties. Metal gains additional resistance to heat and resistance to corrosion processes.
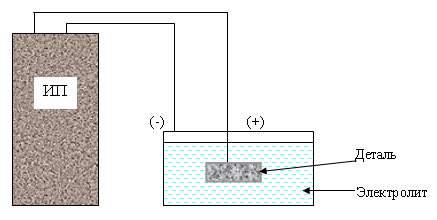
The microarc method is characterized by the use of pulsed or alternating current in a slightly alkaline electrolyte medium. Thus, it is possible to obtain a coating thickness in the region of 200-250 microns. The finished product after processing becomes similar in appearance to ceramic.
Microarc oxidation can also be carried out independently, however, appropriate equipment is required. A feature of the process is its safety for human health. It is this fact that makes the technique more and more popular among home craftsmen.
to contents ↑Features of plasma and thermal processes
Thermal oxidation means the formation of an oxide film in a water vapor or other atmosphere containing acid. In this process is characterized by high temperature.
It is not possible to independently carry out such an operation, since a special expensive furnace is needed where the metal is heated to 350 degrees. However, in this case we are talking about low alloy steels. In the case of medium alloyed and high alloyed steels, the temperature should be even higher - in the region of 700 degrees. The total duration of oxidation by thermal methods is about one hour.
Also, it will not be possible to reproduce the plasma process at home. Such oxidation is carried out in a low-temperature oxygen-containing plasma. The plasma medium itself arises due to microwave and RF discharges. Sometimes direct current is activated. A feature of the technology is the high quality of the products obtained. Therefore, plasma oxidation is used to create high-quality coatings on critical products, which include:
- silicon surfaces;
- semiconductors;
- photocathodes.
Self oxidation
The method described here for creating a protective coating on steel products is available to everyone. First, the part is cleaned and polished. Next, oxides must be removed from the surface (decapitate). Decapitate the part for a minute using a 5% sulfuric acid solution. After dipping, the part must be washed in warm water and passivated (5-minute boiling in a solution of a liter of ordinary water with 50 grams of laundry soap diluted in it). Thus, the surface is prepared for the oxidation procedure.
The sequence of further actions:
- We take a container with an enamel coating. It should not be scratched, it should not be chipped.
- Pour a liter of water into the container and add 50 grams of caustic soda to it.
- We put the container on fire and heat the solution to about 150 degrees.
After 1.5 hours, the part can be removed - oxidation is complete.
to contents ↑Protection of titanium and its alloys
As you know, titanium is notable for its low wear resistance. The oxidation of titanium and alloys based on it increases their antifriction properties, improves the resistance of metal to corrosion.
As a result of applying a protective layer, thick oxide films are formed on the metal (in the range of 20–40 μm), which have enhanced absorption properties.
Structures of titanium alloys are treated at a temperature of 15-25 degrees in a solution comprising 50 grams of sulfuric acid. The current density is 1-1.5 amperes per square decimeter. The duration of the procedure is 50-60 minutes. If the current density exceeds 2 Amperes per square decimeter, the duration of the process is reduced to 30-40 minutes.
During the application of the protective layer, the recommended current density is maintained for the first 3-6 minutes, and the voltage at this time increases to 90-110 V. Upon reaching this indicator, the current density decreases to 0.2 Amperes per square decimeter. Oxidation continues without current regulation. During the process, the electrolyte is mixed. Lead or steel cathodes are used.
to contents ↑
Silver surface protection
Silver oxidation is a method of processing silver products, during which the surface is chemically treated with silver sulfide. The layer thickness is approximately 1 μm. The procedure is carried out in solutions of sulfur compounds. The most common solution is sulfuric liver.
As a result of processing, silver gets an aged look. Its color is from light gray to black or brown. In this case, the thickness of the applied layer affects the color intensity. You can adjust the color during the polishing of the metal - the bulges become light, and the hollows remain darker. Contrast allows you to emphasize the relief of the product. Oxidized silver is sometimes confused with blackened, although the surface treatment technique is different in these cases.
Brass surface protection
The oxidation of brass and bronze products indicates that the parameters of the oxide films and the color of the surfaces are largely dependent on the components of these alloys. For example, with equal amounts of zinc and tin in the bronze metal, the oxide film is difficult to form, but when lead is added, the quality of the oxide film increases sharply. When treating brass with ammonium sulfide, alloys with a high level of zinc are more difficult to oxidize than brass containing not more than 10% zinc.
The long-used formulation based on the so-called sulfuric liver is now modified: now, after the crystals are dissolved, ammonium sulfide is added to it. Based on the amount of solution, you can get a different color of the oxide film: from light brown to dark brown or even black. Moreover, the film is obtained of excellent quality and uniform color.
Also, a 10% thiocarbonate solution can be used to process alloys. However, the solution is only used for brass and bronze with a low zinc content.
Another way to protect the bronze surface and make it look attractive is to use sodium thioantimonate. As a result, a uniformly coated film with a reddish tint is obtained.
Oxidation is a process that requires in-depth knowledge of chemical-physical processes and, as a rule, expensive equipment. However, the simplest technology for applying a protective film is available to everyone, it is enough to follow the simple instructions described in this article.










Apparently, the authors did not do what they wrote about. Water boils at 100 degrees, dissolving 50 grams of sodium hydroxide in 1 liter. water you do not heat it to 140 degrees